Could technology companies eliminate the need for any more power plants to be built in the United States for the next decade? Peak demand dictates the need for generating capacity. Therefore, a significant amount of the capacity is idle most of the time. A smart grid could increase the efficiency of electricity generation and distribution in the US.
Based on data from 2002-2012, the Energy Industry Association (EIA) estimates that US capacity typically exceeds theoretical peak demand by about 20%. The excess capacity is necessary because plants can experience maintenance or unexpected problems at any time. Based on regulatory guidelines for spare capacity, peak demand typically exceeds the average load on the grid by about 80%. As shown in the chart below, the end result is that the total generating capacity is more than double the average load.
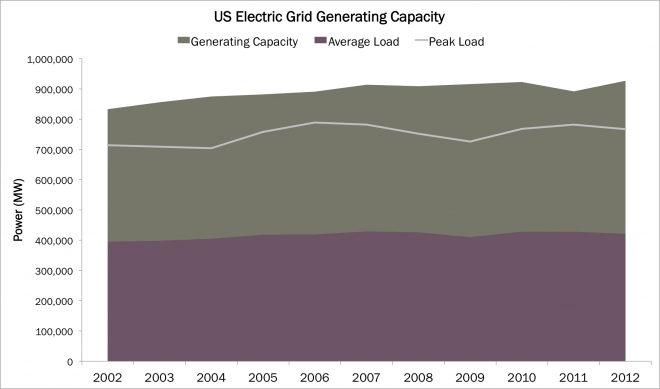
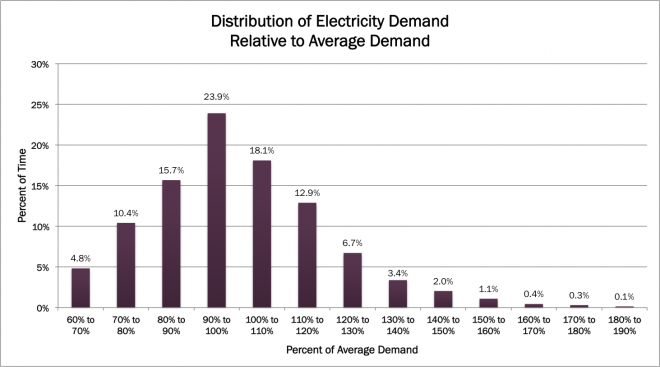
Clearly, the distribution of electricity demand is not constant over time. As the histogram below illustrates, the minimum electricity load in 2013 was about 36% below the average load, and the maximum load about 85% higher. Rarely does peak demand reach the upper end of the range. In fact, only 2% of the time was energy demand in the top 30% of the range. [1]
Movements towards a smart grid could change this dynamic. Hoping to defer building new power plants to meet increases in peak demand, some utilities are experimenting with technologies to smooth the demand for electricity. For example, Oklahoma Gas and Electric (OG&E) has been running a demand response program that provides households with smart meters and programmable thermostats such as the Google [GOOG] Nest. OG&E combines the offer with a variable pricing model in which the highest prices correspond to peak demand. In the initial results, participating customers reduced their electricity usage during periods of peak demand by roughly 20% (1.3 kW) on average.
If 10% of the 127 million households were to participate in such a program and experience similar results, peak demand would be 2% (16.5 gW) lower in the US. That small reduction would eliminate the need for 29 conventional natural gas power stations (about 620 mW each). Those plants cost $16 billion to build, and an additional $240 million annually to operate.
Just image how much more efficient utilities would be if they adopted demand response programs and helped building out a new age smart grid in the United States. Perhaps utilities will see the light, and early-stage companies such as Silver Spring Networks [SSNI] and Echelon [ELON] will find success after all.

 Actively Managed Equity
Actively Managed Equity Overview: All Strategies
Overview: All Strategies Investor Resources
Investor Resources Indexed Equity
Indexed Equity Private Equity
Private Equity Digital Assets
Digital Assets Invest In The Future Today
Invest In The Future Today
 Take Advantage Of Market Inefficiencies
Take Advantage Of Market Inefficiencies
 Make The World A Better Place
Make The World A Better Place
 Articles
Articles Podcasts
Podcasts White Papers
White Papers Newsletters
Newsletters Videos
Videos Big Ideas 2024
Big Ideas 2024


